Epigenetic Clocks Predict Disease 30 Years Early

TL;DR: Metabolism isn't fixed—you can manipulate it using science-backed biohacking techniques including time-restricted eating, cold exposure, strategic fasting, smart nutrition timing, and targeted supplements to boost energy, optimize weight, and enhance metabolic health.

Your body burns calories every second you're alive, but what if you could dial up that furnace? Metabolism isn't some fixed trait you're stuck with. It's a dynamic system you can actively manipulate using evidence-based techniques that researchers have spent decades refining. Whether you're chasing weight loss, boundless energy, or just want to optimize how your cells convert fuel into life, the tools exist right now to rewire your metabolic engine.
Before you start experimenting, you need to understand what you're tweaking. Your basal metabolic rate, the energy you burn at complete rest, accounts for 60-75% of your total daily expenditure. It's determined by factors you can't change, like genetics and age, but also by levers you absolutely can pull.
Muscle tissue torches calories even when you're sitting still. Brown adipose tissue, a specialized fat that generates heat rather than storing energy, can produce up to 300 watts per kilogram when activated—vastly outpacing the measly 1 watt per kilogram from other tissues. Your thyroid hormones set the pace for cellular energy production. Insulin sensitivity determines how efficiently you process fuel. And your gut microbiome, the trillions of bacteria living in your digestive tract, orchestrates metabolic signaling in ways scientists are just beginning to decode.
Research from a 5-year study tracking over 16,000 non-obese adults found that each unit increase in BMR raised liver disease risk by 30%, highlighting that metabolic rate isn't just about weight. It's a biomarker for systemic health, meaning the strategies you use to boost it need to be smart, not reckless.
Your metabolism doesn't run on a flat schedule. It follows a 24-hour rhythm dictated by your internal clock, and when you eat matters as much as what you eat. Time-restricted feeding—limiting your daily eating window—restores the natural oscillation of metabolic hormones and gut bacteria.
A 12-week trial in adults with type 2 diabetes showed that a 10-hour eating window reduced HbA1c by 0.7% and increased populations of beneficial bacteria that produce short-chain fatty acids. These compounds fuel your gut lining, reduce inflammation, and improve insulin sensitivity. No calorie counting. No special foods. Just eating within a consistent window each day.
The mechanism is elegant: when you align meals with your body's circadian clock, you synchronize the rhythms of clock genes in your liver, pancreas, and adipose tissue. This coordination optimizes glucose metabolism during daylight hours when insulin sensitivity naturally peaks. Late-night eating, by contrast, disrupts these rhythms and promotes fat storage because your body expects to fast overnight.
Research from the University of Barcelona found that the timing of your last meal is critical. Eating within two hours of bedtime impairs glucose regulation the following morning, while finishing dinner by early evening preserves metabolic flexibility. The fix is simple: front-load your calories, eat your largest meals earlier in the day, and let your digestive system rest for at least 12 hours overnight.
Social jetlag—the mismatch between your weekday and weekend sleep schedules—wreaks havoc on this system. Just 1.5 hours of sleep timing inconsistency reduces SCFA-producing gut bacteria and elevates inflammatory markers. If you want to biohack your metabolism, consistency in meal timing and sleep schedule is non-negotiable.
Humans evolved to generate heat when cold, and that ancient survival mechanism is now a metabolic tool. Cold exposure activates brown adipose tissue, which burns glucose and fat to produce warmth. Unlike white fat that stores energy, BAT dissipates it.
A controlled study measured what happens when people take mirabegron, a drug that mimics cold-induced BAT activation, in a 20°C environment. Resting energy expenditure jumped by 8% over six hours. That might sound modest, but it compounds. If you can safely boost daily calorie burn by 150-200 calories through thermogenesis alone, that's roughly a pound of fat loss every 20 days without changing your diet.

You don't need drugs. Cold showers, ice baths, and outdoor winter exposure all trigger the same pathways. The key is gradual adaptation. Start with 30 seconds of cold water at the end of your shower. Progress to full cold showers, then brief ice baths. As your body adapts, you'll shiver less because your BAT becomes more efficient at generating heat without the muscle contractions.
One practical approach: cold water immersion for 11 minutes per week, split across multiple sessions. This protocol, popularized by researchers studying deliberate cold exposure, triggers norepinephrine release—a neurotransmitter that not only activates BAT but also sharpens focus and mood.
Safety matters. Don't jump straight into ice baths if you have cardiovascular issues. The shock can spike heart rate and blood pressure. Monitor how you feel, start conservatively, and consult a doctor if you have any underlying conditions. The mirabegron study documented small but significant increases in heart rate and blood pressure, reminding us that thermogenic interventions are physiologically potent.
Fasting isn't about deprivation. It's about teaching your body to burn stored fat when food isn't available. Most people live in a constant fed state, snacking throughout the day, which keeps insulin chronically elevated and locks fat inside cells. Intermittent fasting breaks that cycle.
The 18:6 protocol—fasting for 18 hours, eating within a 6-hour window—is one of the most studied approaches. During the fasting period, insulin drops, growth hormone rises, and your cells shift from glucose to fatty acids as their primary fuel. This metabolic flexibility is the hallmark of a healthy metabolism.
A BMJ meta-analysis reviewing dozens of trials found that intermittent fasting reduces body weight by 3-8% over 8-24 weeks, with particular effectiveness for visceral fat—the dangerous fat around organs linked to metabolic disease. But weight loss is just one outcome. Fasting also triggers autophagy, a cellular cleanup process that removes damaged proteins and organelles, potentially extending healthspan.
Start with a 12:12 pattern—12 hours fasting, 12 hours eating. Most people already do this if they finish dinner by 8 PM and don't eat breakfast until 8 AM. From there, gradually extend the fasting window. Pay attention to hunger cues. True hunger is a dull sensation in your stomach, not cravings or low energy, which are often signs of blood sugar dysregulation that improve as you adapt.
Women may need to adjust fasting protocols around their menstrual cycle, as hormonal fluctuations affect metabolic responses. Some evidence suggests that shorter fasting windows or cyclical fasting—fasting intensely for a few days then eating normally—better supports female hormonal health.
Combine fasting with circadian alignment for maximum impact. If you're doing 16:8, eat between 10 AM and 6 PM rather than noon to 8 PM. Early time-restricted feeding improves insulin sensitivity more than late-shifted windows because it aligns calorie intake with peak metabolic hours.
Beyond when you eat, what you eat and in what proportion fundamentally shapes metabolic rate. Protein has the highest thermic effect of food—your body burns 20-30% of protein calories just digesting and processing it, compared to 5-10% for carbs and 0-3% for fat.
A high-protein diet (1.6-2.2 grams per kilogram of body weight) preserves muscle during weight loss, and since muscle is metabolically active tissue, maintaining it keeps your BMR elevated. Leucine, an amino acid abundant in animal proteins, directly stimulates muscle protein synthesis and mitochondrial biogenesis.
Carbohydrate timing can optimize performance and recovery without derailing fat loss. Consuming carbs around training sessions—before for fuel, after for recovery—channels glucose into muscle glycogen instead of fat storage. On rest days, lower carb intake and increase healthy fats to encourage fat oxidation.
Omega-3 fatty acids from fish, flax, and algae reduce inflammation and improve mitochondrial function, the energy-producing structures in your cells. Mitochondria are the engines of metabolism, and their health determines how efficiently you convert nutrients into ATP. Antioxidants from colorful vegetables protect mitochondria from oxidative damage.
One emerging strategy involves strategic refeeds—periodic high-carb days during extended calorie restriction. These temporarily spike leptin, a hormone that signals energy availability to your brain, preventing the metabolic slowdown that typically accompanies dieting. Research is still evolving on optimal refeeding frequency, but many practitioners use weekly or biweekly refeeds during aggressive fat loss phases.

Supplements can't replace solid fundamentals, but certain compounds have legitimate metabolic effects backed by research. Caffeine increases energy expenditure by 3-11% and enhances fat oxidation, particularly when consumed before exercise. Green tea extract, specifically the catechin EGCG, boosts metabolism modestly and may enhance fat breakdown.
L-carnitine shuttles fatty acids into mitochondria for burning. While your body produces it, supplementation (1-2 grams daily) can support fat metabolism, especially in people with low baseline levels or those following plant-based diets.
Vitamin D deficiency impairs insulin function and correlates with lower metabolic rate. Most people living far from the equator need supplementation, typically 2,000-4,000 IU daily, to maintain optimal levels. Magnesium is a cofactor in over 300 enzymatic reactions, including those involved in energy production. Deficiency is common and can manifest as fatigue and poor glucose control.
Iodine and selenium support thyroid hormone synthesis. The thyroid is your metabolic thermostat, and insufficient micronutrients can lead to sluggish thyroid function even in the absence of clinical disease. A Brazil nut or two daily covers selenium needs, while iodized salt or seaweed provides iodine.
Some biohackers experiment with berberine, a plant compound that activates AMPK, an enzyme that regulates energy balance. Studies show it can lower blood sugar and improve insulin sensitivity comparable to metformin, but it also interacts with medications, so medical supervision is wise.
Creatine isn't just for muscle building. It supports ATP regeneration and may enhance cognitive function and metabolic resilience. Standard dosing is 3-5 grams daily.
Don't fall for proprietary blends or miracle pills. The supplement industry is rife with overpromising and underdelivering. Stick with single-ingredient, third-party tested products, and remember that supplements are amplifiers of good habits, not replacements.
High-intensity interval training spikes metabolic rate acutely during exercise and keeps it elevated for hours afterward through excess post-exercise oxygen consumption. A 20-minute HIIT session can burn as many calories as an hour of steady cardio while also building muscle and improving insulin sensitivity.
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy—breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized chamber—may enhance mitochondrial function by increasing oxygen delivery to tissues. While promising, it's expensive and accessibility is limited. The evidence base is growing but not yet conclusive for metabolic optimization in healthy individuals.
Some biohackers focus on directly supporting mitochondria through nutrients like CoQ10, PQQ, and alpha-lipoic acid. These compounds function as electron carriers and antioxidants in the mitochondrial membrane. Dave Asprey advocates for spirulina and chlorella, algae rich in phytonutrients that support detoxification and energy production, though rigorous human trials are still needed.
Deliberate heat exposure—saunas—works synergistically with cold. Regular sauna use (15-20 minutes at 175-195°F, several times per week) induces heat shock proteins that protect cells from stress, improve cardiovascular function, and may boost growth hormone secretion. Alternating hot and cold exposure, a practice rooted in Scandinavian tradition, trains your body's thermoregulatory systems and enhances resilience.
Biohacking your metabolism isn't without risk. Aggressive calorie restriction slows metabolism over time as your body adapts to scarcity. Metabolic adaptation is real: studies on weight loss show that people maintaining significant weight loss burn 100-500 fewer calories per day than predicted by their new body size.
The solution is reverse dieting—gradually increasing calories after a diet to rebuild metabolic rate without rapid fat regain. Add 50-100 calories per week, prioritizing protein and whole foods, while monitoring weight and energy levels.
Overtraining syndrome can crash metabolism. Exercise is a stressor, and without adequate recovery, chronic cortisol elevation drives muscle breakdown and metabolic dysfunction. More is not always better. Prioritize sleep, manage life stress, and take rest days seriously.
Thyroid manipulation through exogenous hormones or excessive iodine is dangerous. Don't self-prescribe thyroid medication or megadose supplements hoping to "hack" your thyroid. Dysregulation can cause heart arrhythmias, bone loss, and anxiety.
Watch for signs you're pushing too hard: persistent fatigue, irritability, insomnia, loss of menstrual cycle in women, or declining performance. These indicate your body is under chronic stress and cannot sustain the interventions you're using.
Consult healthcare professionals before major changes, especially if you have metabolic disorders, cardiovascular disease, or are taking medications. Blood work can reveal baseline metrics like thyroid function, vitamin D, and HbA1c, allowing you to track whether your interventions are working.
There's no universal prescription because metabolism is individual. Genetics, age, sex, training history, stress levels, and sleep quality all modulate how you respond to interventions. Start with the fundamentals that have the strongest evidence and lowest risk.
Prioritize sleep. Seven to nine hours per night, with consistent timing, is foundational. Poor sleep disrupts hunger hormones, impairs glucose metabolism, and reduces energy expenditure.
Eat within a consistent window aligned with daylight. A 10-12 hour eating window is a good starting point. If that feels easy, progress to 16:8 or 18:6.
Incorporate cold exposure gradually. End showers with 30-60 seconds of cold. Build to full cold showers or weekly ice baths.
Lift weights 3-4 times per week to build or maintain muscle mass. Add HIIT 1-2 times per week for metabolic conditioning.
Consume adequate protein (1.6-2.2 g/kg body weight), prioritize whole foods, and time carbs around activity.
Consider basic supplements: vitamin D, magnesium, omega-3s, and caffeine if well-tolerated.
Track metrics that matter: energy levels, sleep quality, strength progression, body composition, and bloodwork. Adjust based on data, not guesswork.
We're in the early innings of understanding metabolism. Emerging technologies like continuous glucose monitors, wearable metabolic trackers, and genetic testing are democratizing access to data that was once confined to research labs. You can now see in real time how different foods, fasting windows, and exercise sessions affect your glucose and ketone levels.
Personalized nutrition based on microbiome composition and genetic variants is moving from concept to reality. Companies are beginning to offer tailored dietary recommendations based on DNA analysis and gut bacteria profiles, though the science is still maturing.
Pharmacological tools like GLP-1 agonists (semaglutide, tirzepatide) are proving remarkably effective for weight loss by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing appetite. While primarily used for obesity and diabetes, they're being explored for metabolic optimization in broader populations. The ethical and accessibility questions around these medications are still being debated.
Senolytic therapies that clear senescent cells—dysfunctional cells that accumulate with age and disrupt metabolism—are in early human trials. If successful, they could restore youthful metabolic flexibility in aging populations.
But the most powerful tool remains behavior. Metabolism responds to the signals you send through food, movement, temperature, and sleep. No pill can replace the metabolic benefits of muscle-building exercise, circadian alignment, and stress management.
The biohackers who succeed long-term aren't those chasing exotic interventions. They're the ones who master the basics and sustain them. Your metabolism isn't a problem to solve once and forget. It's a system to optimize continuously as you age, as science evolves, and as your goals change.
Pick one intervention. Don't overhaul your entire life overnight. If you're new to this, start with circadian-aligned eating or cold showers. Master it for a month. Measure the impact. Then add another layer.
Track your progress. Use a journal, app, or spreadsheet. Record what you do, how you feel, and objective markers like body weight, waist circumference, or performance metrics. Data reveals patterns that intuition misses.
Experiment systematically. Change one variable at a time so you know what's working. If you start fasting, cold exposure, and a new supplement simultaneously and feel great, you won't know which intervention deserves the credit.
Listen to your body. Biohacking is not about punishment. If an intervention leaves you feeling worse, drained, or obsessive, reassess. The goal is vitality, not martyrdom.
Stay curious and skeptical. Science is self-correcting. A study today might be contradicted tomorrow. Read the research, but weigh it against your personal experience. Your metabolism is the ultimate laboratory.
The human body is an adaptive machine. It responds to the inputs you provide. By understanding the science and applying evidence-based techniques, you can unlock energy, resilience, and longevity that most people leave on the table. Your metabolic potential is far greater than you think. It's time to tap into it.
Recent breakthroughs in fusion technology—including 351,000-gauss magnetic fields, AI-driven plasma diagnostics, and net energy gain at the National Ignition Facility—are transforming fusion propulsion from science fiction to engineering frontier. Scientists now have a realistic pathway to accelerate spacecraft to 10% of light speed, enabling a 43-year journey to Alpha Centauri. While challenges remain in miniaturization, neutron management, and sustained operation, the physics barriers have ...

Epigenetic clocks measure DNA methylation patterns to calculate biological age, which predicts disease risk up to 30 years before symptoms appear. Landmark studies show that accelerated epigenetic aging forecasts cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and neurodegeneration with remarkable accuracy. Lifestyle interventions—Mediterranean diet, structured exercise, quality sleep, stress management—can measurably reverse biological aging, reducing epigenetic age by 1-2 years within months. Commercial ...

Data centers consumed 415 terawatt-hours of electricity in 2024 and will nearly double that by 2030, driven by AI's insatiable energy appetite. Despite tech giants' renewable pledges, actual emissions are up to 662% higher than reported due to accounting loopholes. A digital pollution tax—similar to Europe's carbon border tariff—could finally force the industry to invest in efficiency technologies like liquid cooling, waste heat recovery, and time-matched renewable power, transforming volunta...

Humans are hardwired to see invisible agents—gods, ghosts, conspiracies—thanks to the Hyperactive Agency Detection Device (HADD), an evolutionary survival mechanism that favored false alarms over fatal misses. This cognitive bias, rooted in brain regions like the temporoparietal junction and medial prefrontal cortex, generates religious beliefs, animistic worldviews, and conspiracy theories across all cultures. Understanding HADD doesn't eliminate belief, but it helps us recognize when our pa...
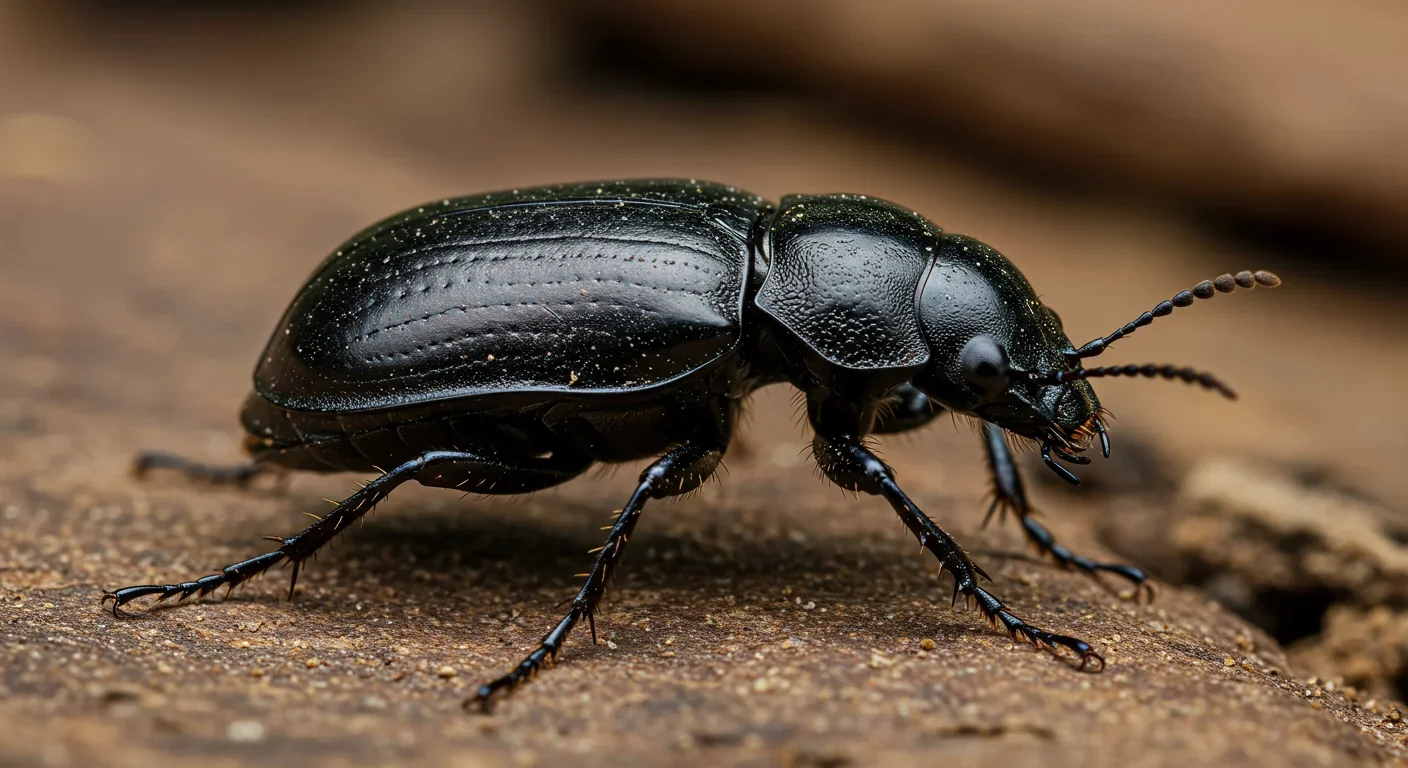

The bombardier beetle has perfected a chemical defense system that human engineers are still trying to replicate: a two-chamber micro-combustion engine that mixes hydroquinone and hydrogen peroxide to create explosive 100°C sprays at up to 500 pulses per second, aimed with 270-degree precision. This tiny insect's biochemical marvel is inspiring revolutionary technologies in aerospace propulsion, pharmaceutical delivery, and fire suppression. By 2030, beetle-inspired systems could position sat...

The U.S. faces a catastrophic care worker shortage driven by poverty-level wages, overwhelming burnout, and systemic undervaluation. With 99% of nursing homes hiring and 9.7 million openings projected by 2034, the crisis threatens patient safety, family stability, and economic productivity. Evidence-based solutions—wage reforms, streamlined training, technology integration, and policy enforcement—exist and work, but require sustained political will and cultural recognition that caregiving is ...

Every major AI model was trained on copyrighted text scraped without permission, triggering billion-dollar lawsuits and forcing a reckoning between innovation and creator rights. The future depends on finding balance between transformative AI development and fair compensation for the people whose work fuels it.