Why Your Brain Sees Gods and Ghosts in Random Events

TL;DR: Groups structured correctly consistently outthink their brightest members through psychological safety, cognitive diversity, and strategic use of AI tools. Organizations unlocking collective intelligence are transforming performance by redesigning meetings, equalizing speaking time, and making work transparent.

Within the next decade, the world's most valuable companies won't be those with the smartest CEOs—they'll be the ones that learned how to amplify their teams' collective brainpower. Research now reveals that groups, when structured correctly, consistently outthink even their brightest individual members. From Google's groundbreaking Project Aristotle to the open-source communities building tomorrow's technology, collective intelligence has become the hidden competitive advantage separating market leaders from everyone else.
Collective intelligence isn't just corporate jargon—it's a measurable phenomenon rooted in cognitive science. When researchers studied decision-making patterns across thousands of teams, they discovered something surprising: a group's collective IQ depends less on individual brilliance than on how members interact.
The key factor? What psychologists call social sensitivity—the ability to pick up on subtle emotional and social cues. Teams where members actively listen, take turns speaking, and read each other's body language score significantly higher on collective problem-solving tasks. One team member dominating conversations, even if they're the smartest person in the room, actually drags down group performance.
Studies measuring collective intelligence found that diversity of thought matters more than diversity of expertise. A team of five domain experts often gets outperformed by a mixed group combining experts with informed generalists. Why? Because homogeneous groups fall into predictable thinking patterns, while cognitively diverse teams challenge assumptions and explore solution spaces others miss.
The math works in teams' favor: research shows groups aggregate information more effectively than individuals when making predictions. Prediction markets, which harness collective intelligence from thousands of participants, consistently outperform individual expert forecasts on everything from election outcomes to product launches. The crowd doesn't just match expert accuracy—it beats it.
But there's a catch. Groups can also amplify biases and make spectacularly bad calls. Groupthink, the tendency for teams to prioritize harmony over critical analysis, has torpedoed countless projects. The difference between collective wisdom and collective stupidity comes down to how teams are structured and led.
When Google set out to understand what made some teams exceptional, they expected to find specific combinations of star performers. Instead, Project Aristotle revealed that psychological safety—the shared belief that the team is safe for interpersonal risk-taking—was the single most important factor distinguishing high-performing teams.
Teams with psychological safety don't just feel good. They measurably outperform their peers because members freely admit mistakes, ask questions, and propose half-formed ideas without fear of embarrassment. This creates a feedback-rich environment where problems get identified and solved faster.
But Google's research also uncovered a nuance: psychological safety alone isn't enough. Teams also need what researchers call "high courage"—the willingness to tackle uncomfortable conversations. Many teams create pleasant, supportive environments where people still avoid addressing the toughest issues. The magic happens when safety combines with courage to discuss the "last 8%" of what actually needs to be said.
The data backs this up. In Google's analysis, teams demonstrating both psychological safety and constructive conflict resolution completed projects 25% faster and with higher quality ratings. The psychological safety provided the foundation, but productive disagreement pushed solutions forward.

Open-source communities provide a natural laboratory for collective intelligence at scale. Projects like Linux, which powers most of the internet, or Wikipedia, which aggregated human knowledge faster than any previous encyclopedia, demonstrate collective intelligence working across thousands of contributors who've never met.
What makes these communities work? First, radical transparency. DevOps practices that emerged from open-source culture emphasize visible workflows, shared documentation, and peer review of every contribution. When everyone can see the whole system, local innovations spread faster and duplicated efforts get eliminated.
Second, merit-based hierarchies. In open source, your ideas carry weight based on their quality and your track record, not your job title. This creates what researchers call "stigmergic coordination"—self-organization through indirect communication. Contributors see what others are building and automatically fill gaps without centralized direction.
Third, low barriers to contribution. The best open-source projects make it easy to start small. You don't need permission to fix a typo, propose an idea, or fork a project. This reduces the coordination costs that typically limit collective action, allowing thousands of micro-contributions to compound into major innovations.
Compare this to traditional corporate hierarchies, where brilliant ideas from junior employees routinely die in approval chains. Open source flips that model, testing ideas in production rather than in committee meetings.
Artificial intelligence isn't replacing collective intelligence—it's supercharging it. When Microsoft integrated AI agents into Teams, they found something unexpected: teams using AI collaboratively outperformed both traditional teams and individuals using AI alone.
The reason reveals something fundamental about human-AI collaboration. AI excels at pattern recognition and information synthesis, but struggles with context, judgment, and creative leaps. Humans bring domain expertise and intuitive understanding but get overwhelmed by data volume. Together, they cover each other's blind spots.
Recent research on augmented intelligence shows that AI tools amplify collective intelligence most when they're designed for collaboration rather than automation. Instead of replacing human decision-makers, AI surfaces relevant information, highlights patterns, and simulates scenarios—letting teams make better-informed choices faster.
Interestingly, unequal AI access within teams can enhance productivity. When some team members have advanced AI tools while others don't, it creates natural knowledge-sharing opportunities. The AI-equipped members introduce new approaches, and the discussion that follows builds shared understanding better than universal access with less dialogue.
The future of work isn't humans versus machines—it's humans augmented by machines, collaborating together. Teams that master this hybrid model are already pulling ahead.
Most organizations inadvertently suppress collective intelligence without realizing it. The culprit? Structural factors that discourage information sharing and honest feedback.
First, status hierarchies create information bottlenecks. When junior team members hesitate to contradict senior leaders, valuable ground-level insights never reach decision-makers. One study found that teams with steep hierarchies took 40% longer to identify and fix problems because bad news traveled upward slowly or not at all.
Second, performance metrics focused on individual achievement undermine collaborative behavior. If promotions and bonuses reward solo contributions, rational team members hoard knowledge and opportunities. You get brilliant individuals competing rather than a brilliant collective collaborating.
Third, meeting culture often optimizes for efficient information transfer rather than collective thinking. Teams that rush through packed agendas never build the shared understanding required for collective intelligence to emerge. The best teams schedule unstructured time for exploration and debate.
Fourth, remote work creates new challenges for collective intelligence. The casual conversations and spontaneous collaborations that build shared context are harder when everyone's in separate locations. Teams need to deliberately recreate these informal knowledge-sharing channels digitally, or risk fragmenting into isolated individuals.
Even well-intentioned diversity initiatives can backfire. Simply assembling people from different backgrounds doesn't create cognitive diversity—it can create factions. Collective intelligence requires active integration, where diverse perspectives get synthesized into novel solutions rather than just coexisting.

Transforming your team into a high-performing collective intelligence system requires deliberate structural changes. Here's what actually works, based on organizations that have made the transition successfully.
Start by redesigning how meetings work. Research shows that teams achieve higher collective intelligence when they separate divergent thinking (generating ideas) from convergent thinking (evaluating solutions). Structure your sessions accordingly: brainstorming meetings should postpone criticism, while decision meetings should demand rigorous scrutiny.
Implement structured turn-taking. It sounds simple, but ensuring everyone contributes roughly equal speaking time dramatically improves collective problem-solving. One tactic: use a "round-robin" format where each person shares thoughts before opening discussion. This prevents extroverts from dominating and surfaces insights from quieter team members.
Create psychological safety through leader behavior, not policies. When leaders publicly admit uncertainty, ask for feedback on their own ideas, and thank people for respectful disagreement, they model the vulnerability that makes teams safe. IHHP's research shows measurable performance gains within 90 days when leaders adopt these practices consistently.
Leverage decision-making frameworks that aggregate individual judgments effectively. Techniques like Delphi polling—where team members make independent estimates before seeing others' inputs—prevent groupthink while capturing collective wisdom. Follow up with discussion that focuses on outliers, because extreme estimates often reveal information others missed.
Use technology to amplify, not replace, human collaboration. Shared documents with version history, collaborative whiteboards, and AI-powered research assistants help teams build on each other's thinking asynchronously. The goal isn't efficiency—it's making everyone's insights visible and combinable.
Measure what matters. Track metrics like knowledge-sharing frequency, cross-functional collaboration patterns, and how quickly problems surface. Colin Fisher's research demonstrates that teams improve dramatically when they receive feedback on their collaboration patterns, not just their outputs.
The proof isn't just in research studies—it's in organizations transforming performance through collective intelligence.
At Grant Thornton, implementing psychological safety practices led to 32% faster project completion and 28% higher client satisfaction scores. The key change? Leaders started every project with explicit discussions about how the team would handle disagreements and mistakes.
Tech companies embracing open-source collaboration models internally report significant gains. When development teams adopted transparent workflows, visible backlogs, and peer code review, they didn't just catch more bugs—they generated more innovative solutions as developers learned from each other's approaches.
Prediction markets demonstrate collective intelligence at massive scale. Platforms like Kalshi and Polymarket aggregate forecasts from thousands of participants, creating probability estimates that routinely beat traditional polls and expert predictions. Investors have poured funding into these platforms precisely because collective intelligence generates alpha.
Even traditional industries are catching on. Manufacturing companies implementing distributed cognition principles—spreading expertise across teams rather than centralizing in specialists—found that line workers identified process improvements that engineers had missed. When you treat intelligence as a shared field rather than individual property, solutions emerge from unexpected places.
The pattern repeats across sectors: teams that structure for collective intelligence consistently outperform teams relying on individual brilliance.
Knowing collective intelligence matters and building it are different challenges. Start with these concrete steps you can take this week.
First, audit your next three meetings. Track who speaks, for how long, and whose ideas get built upon. If one or two people dominate, implement structured turn-taking immediately. The ROI of psychological safety appears fastest when teams fix conversation imbalances.
Second, introduce pre-meeting individual thinking. Before your next decision meeting, have everyone submit anonymous initial judgments independently. Research confirms this simple change reduces groupthink while preserving the benefits of discussion.
Third, make your work visible. Start using shared documents instead of email attachments. Move conversations from direct messages to channels others can observe and learn from. Transparency compounds collective intelligence over time.
Fourth, schedule reflection sessions focused on how your team works together, not just what you accomplish. Ask: What slowed us down? What helped us think better? Who had insights we didn't fully explore? Teams that reflect on their process improve collaboration patterns faster than those that only review results.
Fifth, bring AI into your team's workflow collaboratively rather than individually. When team members use AI tools together—sharing prompts, critiquing outputs, and building on AI-generated ideas collectively—they develop shared understanding faster than when everyone works in isolation.
The organizations winning in complexity aren't the ones with the smartest individuals. They're the ones that unlocked their teams' collective intelligence—turning groups of smart people into something smarter than any individual could be alone. Your team probably has more potential than you realize. The question is whether you'll build the structures to unleash it.
Recent breakthroughs in fusion technology—including 351,000-gauss magnetic fields, AI-driven plasma diagnostics, and net energy gain at the National Ignition Facility—are transforming fusion propulsion from science fiction to engineering frontier. Scientists now have a realistic pathway to accelerate spacecraft to 10% of light speed, enabling a 43-year journey to Alpha Centauri. While challenges remain in miniaturization, neutron management, and sustained operation, the physics barriers have ...

Epigenetic clocks measure DNA methylation patterns to calculate biological age, which predicts disease risk up to 30 years before symptoms appear. Landmark studies show that accelerated epigenetic aging forecasts cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and neurodegeneration with remarkable accuracy. Lifestyle interventions—Mediterranean diet, structured exercise, quality sleep, stress management—can measurably reverse biological aging, reducing epigenetic age by 1-2 years within months. Commercial ...
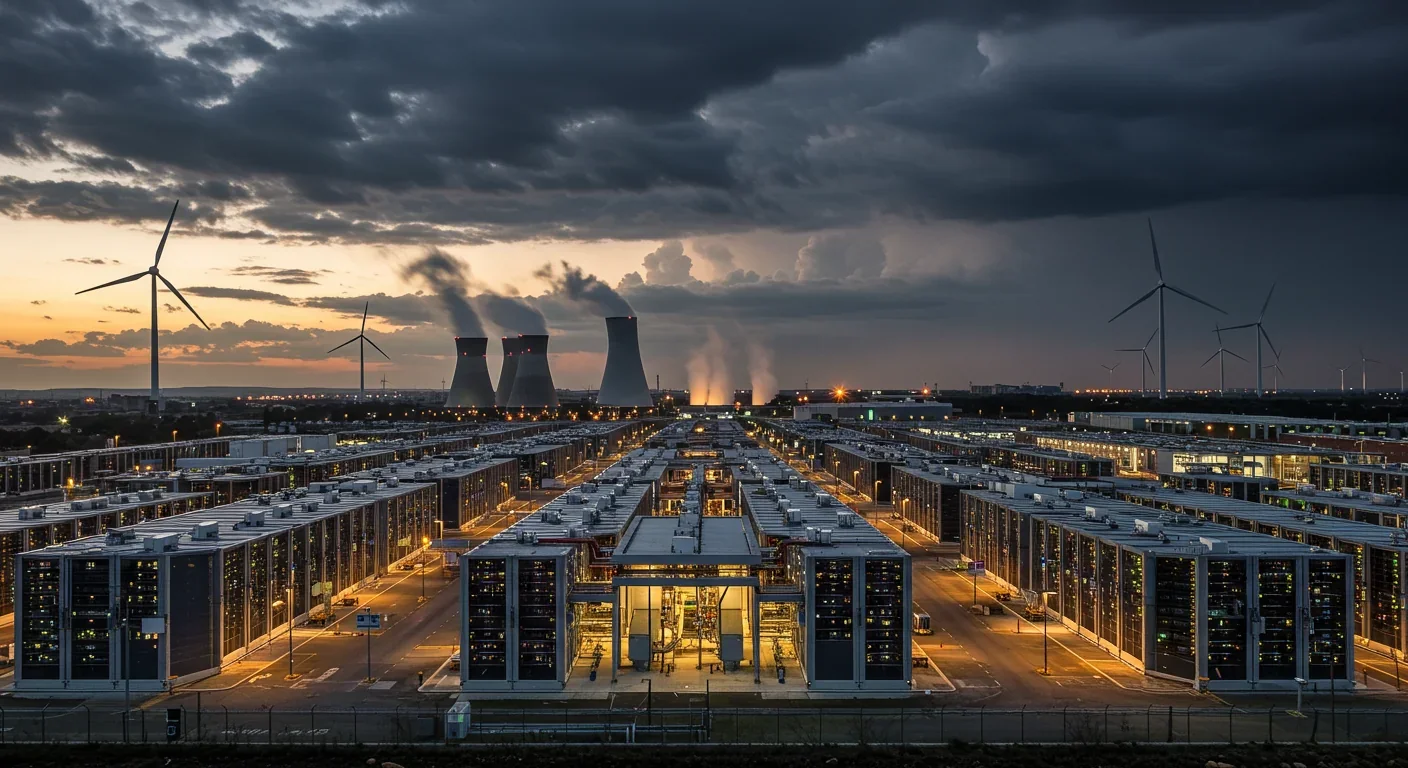

Data centers consumed 415 terawatt-hours of electricity in 2024 and will nearly double that by 2030, driven by AI's insatiable energy appetite. Despite tech giants' renewable pledges, actual emissions are up to 662% higher than reported due to accounting loopholes. A digital pollution tax—similar to Europe's carbon border tariff—could finally force the industry to invest in efficiency technologies like liquid cooling, waste heat recovery, and time-matched renewable power, transforming volunta...

Humans are hardwired to see invisible agents—gods, ghosts, conspiracies—thanks to the Hyperactive Agency Detection Device (HADD), an evolutionary survival mechanism that favored false alarms over fatal misses. This cognitive bias, rooted in brain regions like the temporoparietal junction and medial prefrontal cortex, generates religious beliefs, animistic worldviews, and conspiracy theories across all cultures. Understanding HADD doesn't eliminate belief, but it helps us recognize when our pa...
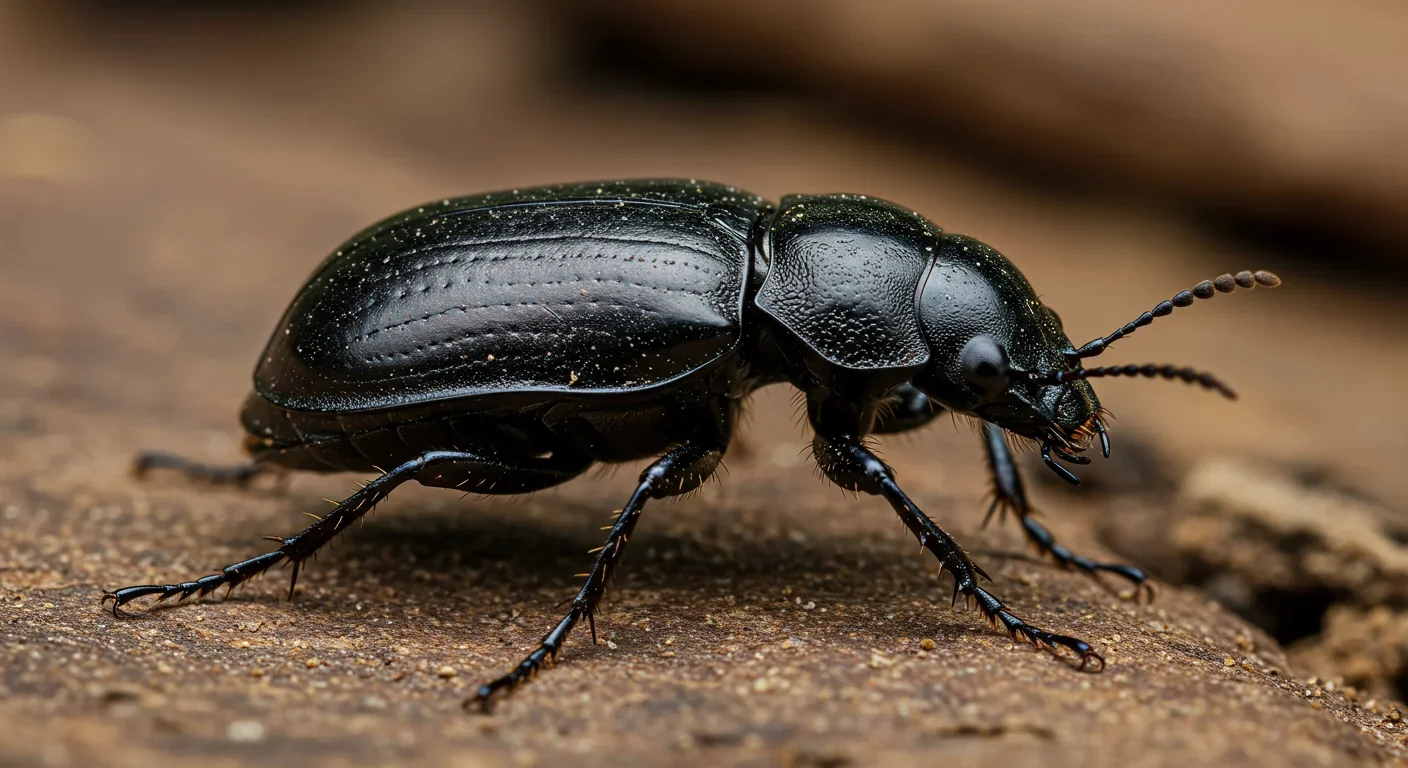

The bombardier beetle has perfected a chemical defense system that human engineers are still trying to replicate: a two-chamber micro-combustion engine that mixes hydroquinone and hydrogen peroxide to create explosive 100°C sprays at up to 500 pulses per second, aimed with 270-degree precision. This tiny insect's biochemical marvel is inspiring revolutionary technologies in aerospace propulsion, pharmaceutical delivery, and fire suppression. By 2030, beetle-inspired systems could position sat...

The U.S. faces a catastrophic care worker shortage driven by poverty-level wages, overwhelming burnout, and systemic undervaluation. With 99% of nursing homes hiring and 9.7 million openings projected by 2034, the crisis threatens patient safety, family stability, and economic productivity. Evidence-based solutions—wage reforms, streamlined training, technology integration, and policy enforcement—exist and work, but require sustained political will and cultural recognition that caregiving is ...

Every major AI model was trained on copyrighted text scraped without permission, triggering billion-dollar lawsuits and forcing a reckoning between innovation and creator rights. The future depends on finding balance between transformative AI development and fair compensation for the people whose work fuels it.